How to find, view and edit video metadata
| March 2, 2021

Metadata may seem opaque and out-of-reach, but it doesn’t have to be. The average person is more than capable of diving into a video file and extracting useful helpful information. This guide is designed to make sure you have all the necessary tools to do so.
What is video metadata?
Video metadata is all available information about a digital video file – like the author, date created, location shot, camera information and upload date. Video metadata helps people who work with video files organize and sort video search results.

Understanding what kind of elements show up as video metadata helps users get a feel for how metadata can help them learn about specific videos. Let’s take a look at how to find and view the metadata of an individual video.
How do I view the metadata of a video?
Now that you have a general idea of what metadata video is, the next important thing to know is a direct path to finding and viewing it. There are a few different methods depending on the type of file and system you’re using, so I’ll go over them all one-by-one. First, we’ll look at the ways to view metadata for video files.
Video files: Using a metadata viewer
The good thing about looking for digital metadata in the age of advanced technology is there are plenty of software systems designed to help you locate and view it without advanced knowledge of computers. Of course, not all systems are created equal. Here are a few that I’ve found to work quite well. Determine which would best suit your personal metadata needs. Additionally, video editing software can also be used to edit a video’s metadata directly.
MediaInfo
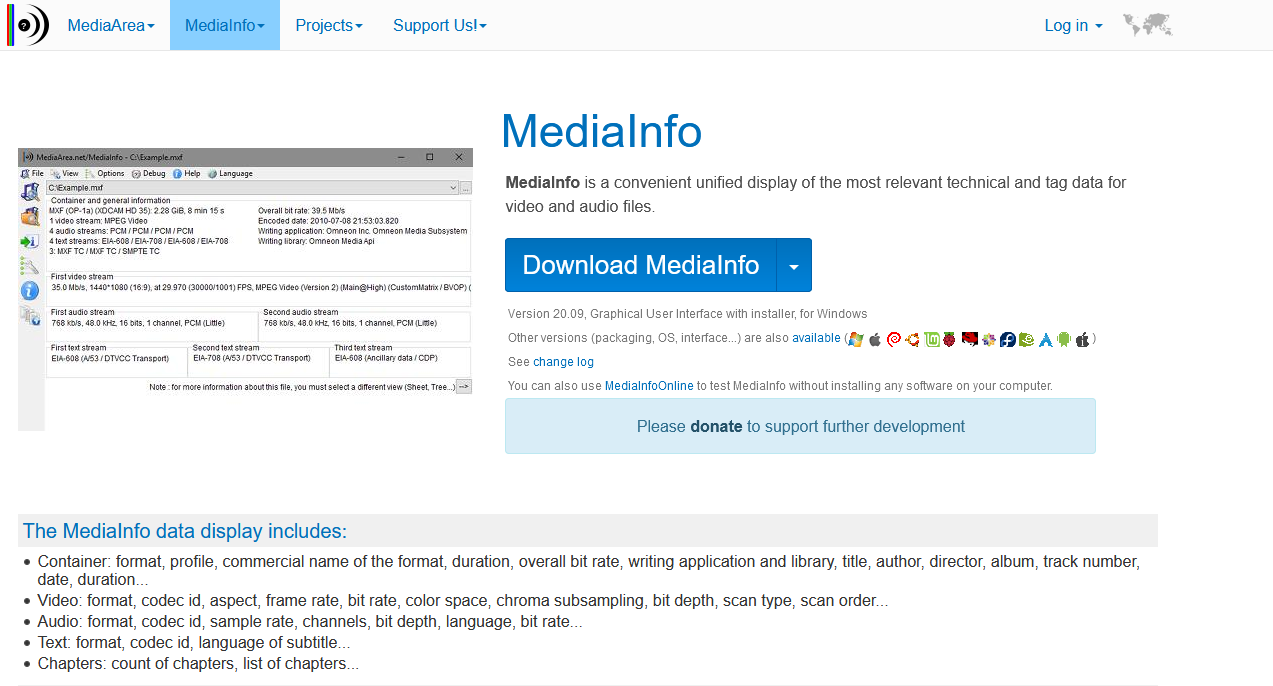
MediaInfo is a downloadable program that pulls metadata from files for the user so they don’t need to do any extra searching to find it. Though it is very in-depth in its ability to locate and display video metadata, it also is capable of managing other media file types. Consider MediaInfo if you want a basic program that is easy to use and accessible on many different platforms. MediaInfo can also display EXIF data, which is standard for image files and important for file organization and searchability.
Wondershare UniConverter
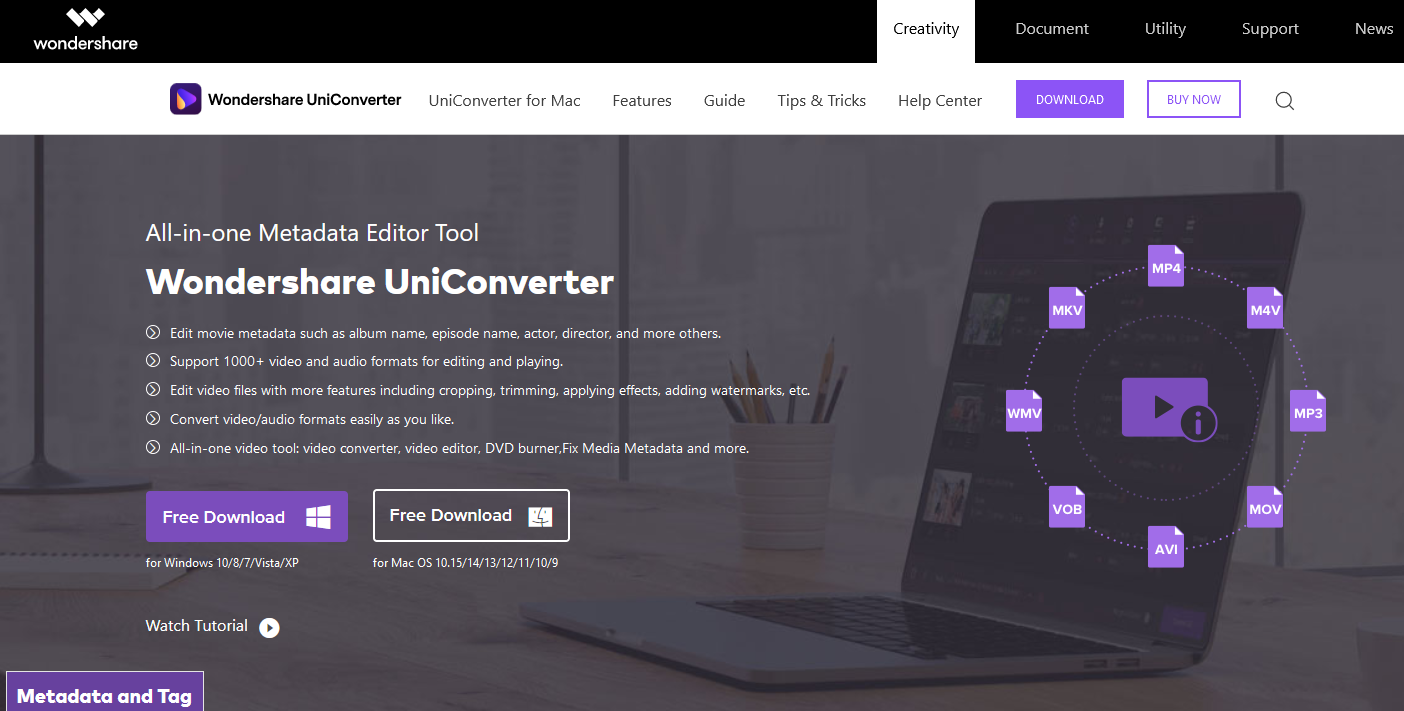
Wondershare UniConverter is one of my favorite programs for viewing video metadata, mostly because of its beautiful, seamless interface. It makes it easy to look at video metadata through the lens of a modern program without excessive technical know-how required. Consider Wondershare if the aesthetic of the program’s interface is a large part of your decision.
Bonus: Metadata2go
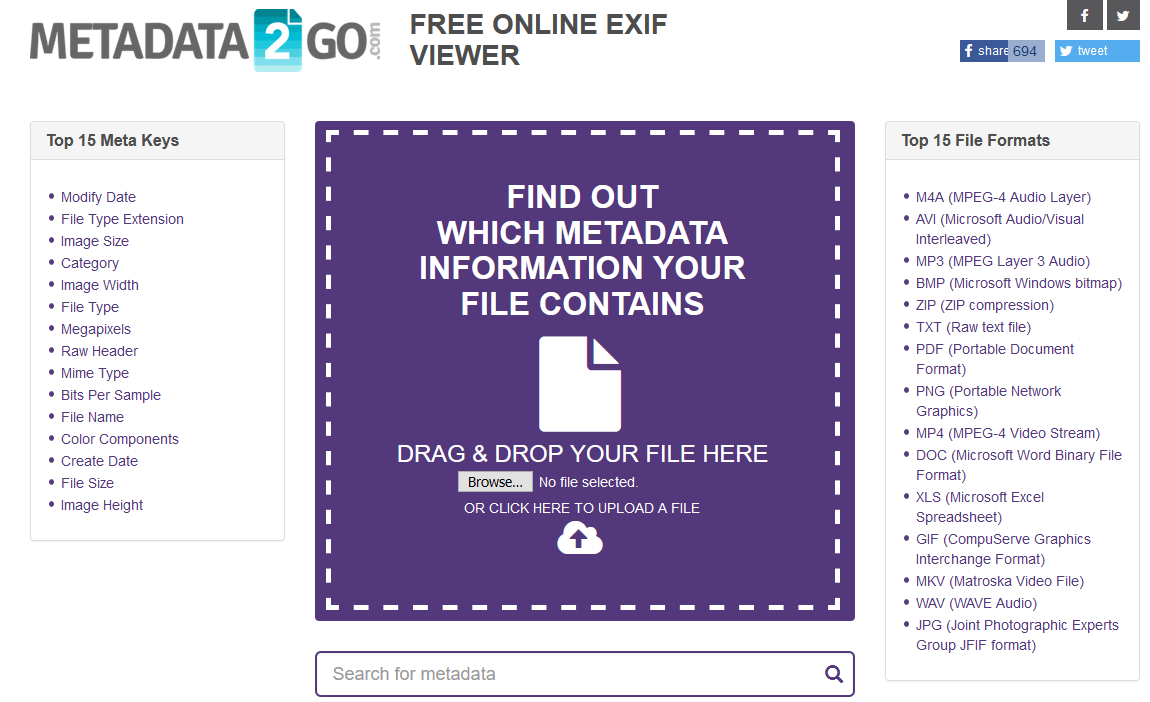
I recommend Metadata2go a lot when metadata comes up, mostly because it represents a clear alternative to other systems, since it requires no download to use. Instead, it’s a cloud-based option that allows you to upload the video file in question and retrieve its metadata. Use Metadata2go if you have limited hard drive space and just need some quick metadata of a video file.
Now that you’re aware of a few systems that excavate metadata, let’s demonstrate how to do so manually.
Video files: Manual approach for Windows
Here’s how to view the metadata of video files if you’re using Windows and don’t have third party software available.
1. Locate the video file you wish to view the metadata of.
2. Right-click the file and select “Properties.”
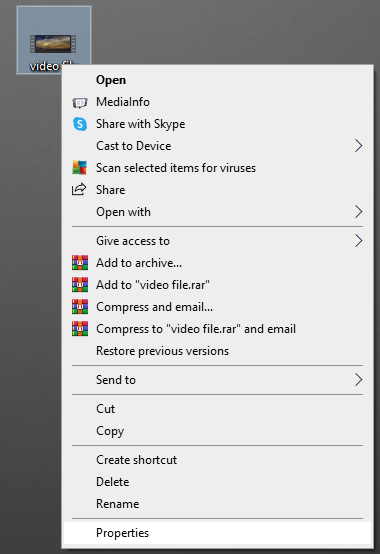
3. Under the “General” tab, you’ll see basic video metadata, such as file size and date created/received.
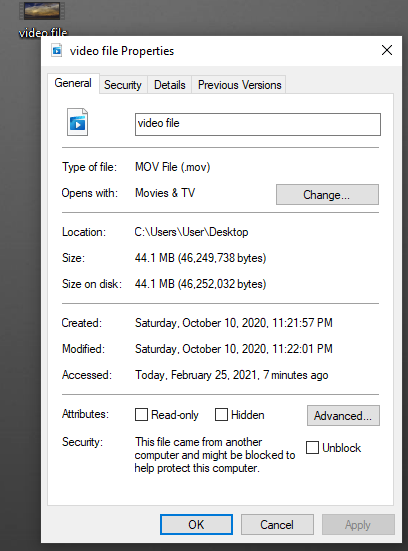
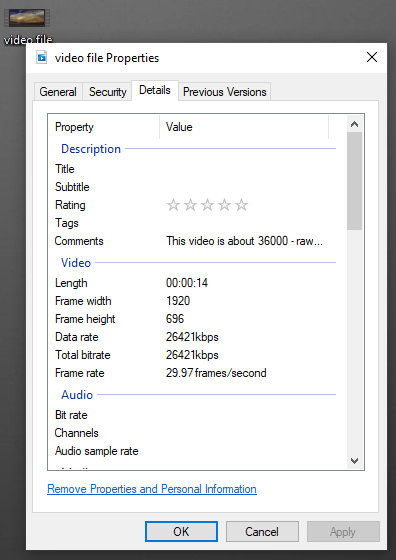
4. Next, click the “Details” tab. This will bring up information such as title, length and frame rate.
Video files: Manual approach for Mac
1. Locate the video file you wish to view the metadata of.
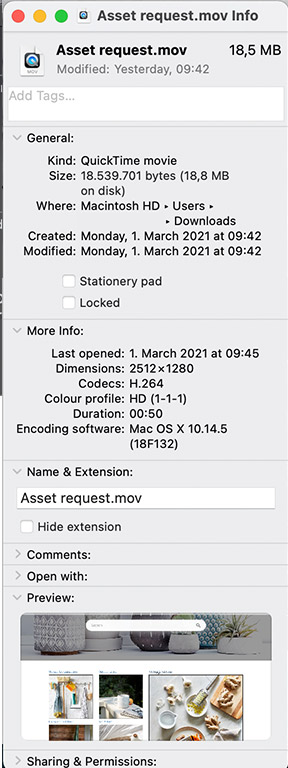
2. Select the “Get info” option.
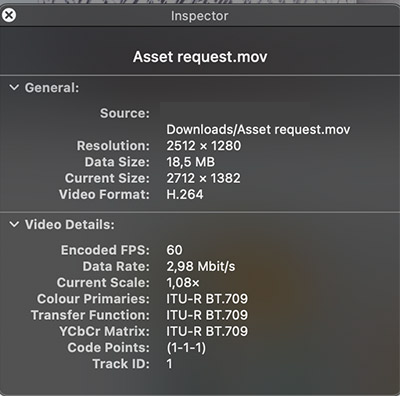
3. If you have specific media software that plays your video files, there may be ways to load the file onto these programs and view metadata as well (specific to each system).
As you can see, there are plenty of different routes to checking out the metadata of a video file. So what about finding metadata for a video uploaded to the internet, for example on YouTube?
Metadata on videos uploaded to YouTube
First things first, recognize that YouTube metadata is different than a video file on your PC. This is because YouTube provides its own set of information on a video when uploaded. Here’s how to check it out.
1. Navigate to the YouTube video you want to find metadata for.
2. Underneath the video screen, there are some basic metadata, such as the title, uploader and date uploaded.
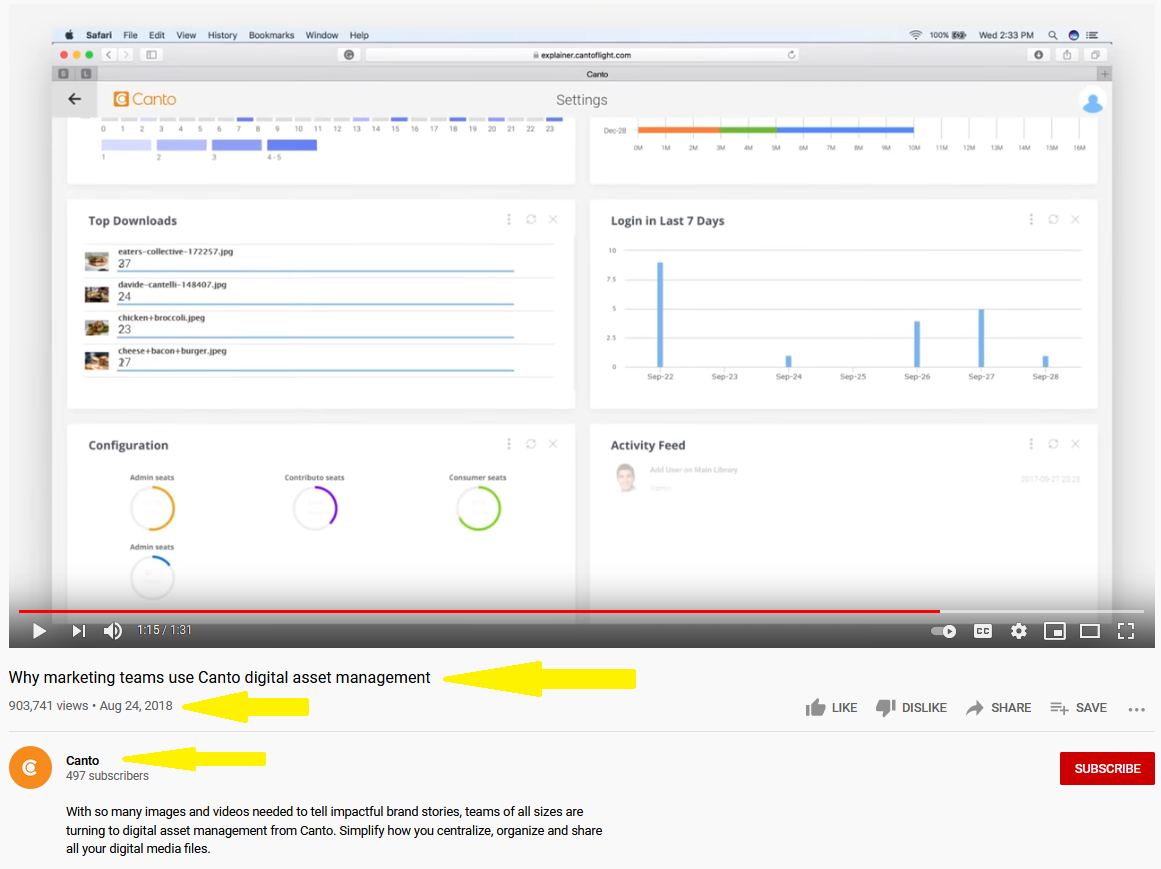
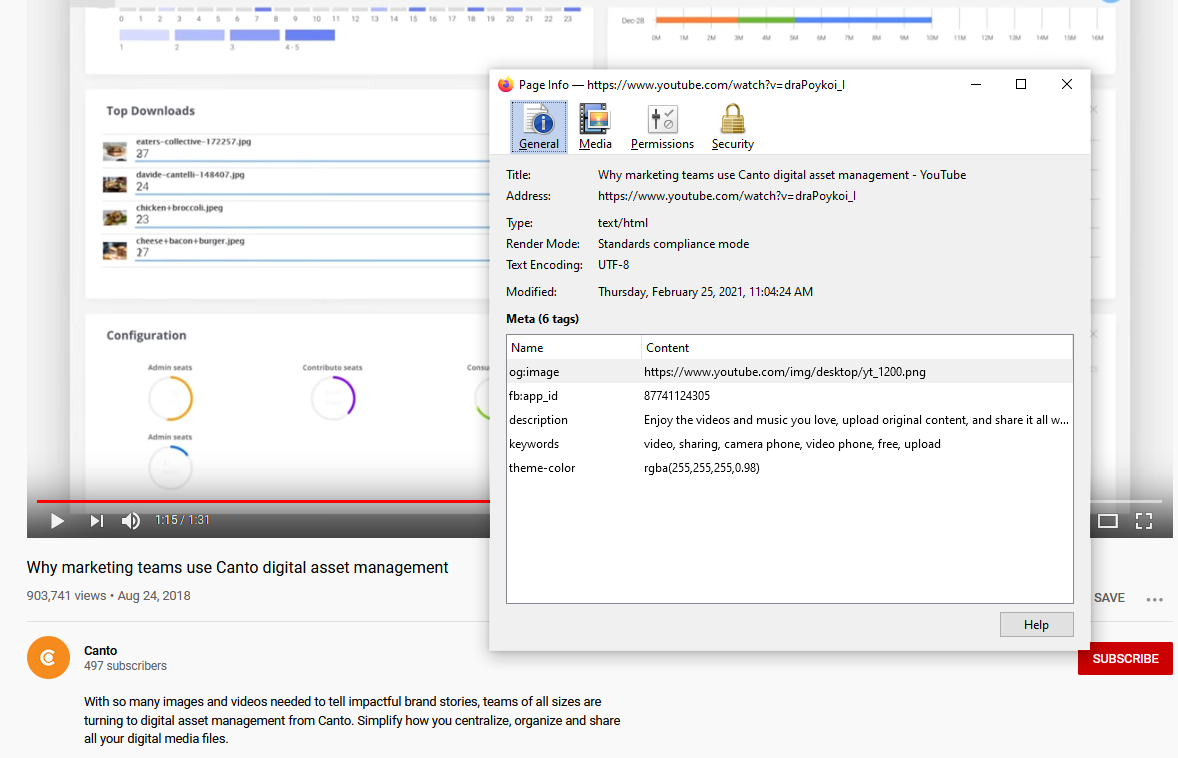
3. To dig deeper, right-click next to the video player and select “View page info.” This will provide you with further details concerning the video, such as the hyperlink and keyword tags.
What can I learn from a video exclusively through metadata?
For whatever reason, the internet has taken a shrine to the concept of metadata in pictures, famously using it to find specific locations like detectives in a novel. However, video metadata hasn’t gotten as much of the same publicity.

However, there are plenty of things you can learn about a video simply by seeing its metadata. Though it would be too difficult to list every possible thing you can find out, I’ll go through some of the basics. Through metadata, you can determine: the type of camera that shot the video, the location it was shot at, the date/time, the size of the file and the editing software used. Structured data must be implemented on web pages to enhance search engine indexing and the creation of rich snippets.
Why is this information valuable?
Most people worry about privacy when it comes to metadata, but the reality is that the information in video files has a lot of cool purposes for different users. For example, if you watched a video of cute puppies and wanted to know the general location it was shot, you could ask the uploader. But if they’re not available or no longer using the platform, you could check the metadata. Things like the camera make/model and editing software could be helpful if you’re interested in creating similar shots in your own videos.
The Importance of Video Structured Data
In the realm of video SEO, video structured data plays a pivotal role. This type of metadata helps search engines like Google understand the content and context of your video files. By embedding structured data, you can significantly enhance the visibility and ranking of your videos in search engine results.
When you add structured data to your video details page, you provide search engines with a clear roadmap of what your video is about. This includes information such as the video title, description, upload date, and even thumbnail images. Search engines use this data to generate rich snippets, which are the enhanced descriptions you see in search results. These snippets can include a video thumbnail, video description, and other relevant details, making your video more appealing to users.
Moreover, structured data can help your video appear in specialized search features like video carousels or the video tab on search engines. This increased visibility can drive more traffic to your web page and improve user engagement. For instance, a well-optimized YouTube video with structured data is more likely to appear in the top search results, attracting more viewers.
In summary, incorporating video structured data is not just a technical enhancement but a strategic move to boost your video’s performance in search engine results. By doing so, you ensure that your video content is easily discoverable, leading to higher engagement and better overall video SEO.
Can I edit video metadata with video editing software?
This will be specific to your operating system as well as the third-party media software systems you have installed. Tools like Windows Media Player or the iTunes Player both have options for changing the metadata of video files.
However, if you just want to make minimal changes and don’t want to install metadata editing software, you can right-click a video file, select “Properties,” click the “Details” tab, then find the information section you wish to change. Click underneath the “value” header and enter in the new information.
Manage video metadata efficiently with digital asset management software
For those looking to do more than simply view and edit video metadata, a digital asset management (DAM) platform like Canto DAM is the answer. DAM platforms can help you organize, find, collaborate, and distribute video files with ease using the latest intelligent AI tools. With DAM software, you get:
- Auto-tagging: Organize and tag your content on the fly by visual context. Goodbye clunky metadata management processes.
- Custom metadata: Add relevant metadata visual scanning cannot capture so anyone (including you) can find content quickly.
- AI-powered search: Find and access relevant media instantly using the intelligent AI. No more misplaced or lost videos.
- Facial recognition: Search and retrieve videos featuring specific individuals quickly.

Frequently asked questions
How can I edit advanced metadata fields, such as GPS coordinates or camera-specific data, for a video?
To edit advanced metadata fields like GPS coordinates or camera-specific data, you typically need specialized tools, like professional video editing software, metadata management software, or a digital asset management (DAM) platform. Standard media players and basic tools usually don’t offer this level of editing.
What are the legal or privacy concerns associated with video metadata, especially when sharing content publicly?
Metadata can reveal sensitive information — like location data or details about the device that created the video. It’s important to remove or anonymize metadata to protect privacy, especially when sharing videos publicly.
How do different platforms (like Vimeo or social media) handle video metadata compared to YouTube?
Different platforms handle video metadata differently. YouTube retains and displays only certain types of metadata, like resolution and frame rate. Other platforms like Vimeo or social media sites may strip out detailed metadata to minimize file size and ensure consistent playback across devices. Of course, this can limit how much data is visible to viewers.
