Digital rights management explained: The types and benefits it offers
Digital rights management (DRM) protects digital media from being copied or shared without permission. DRM technology provides tools to control who can access and use copyrighted works or proprietary digital products
DRM technology protects the intellectual property rights of various digital content types, including:
DRM systems protect these products through encryption, licensing agreements, and other technical measures that limit the use of the content and products to authorized users and devices.
How does digital rights management work?
DRM includes code that prevents copying or restricts the time or number of devices on which a user can access a particular product. Sometimes, publishers, companies, and authors use an application that encrypts the media, software, or content. Only users who have the decryption keys can access the content.
DRM also lets you access a log of people and times when assets were used. For example, you could see when software was downloaded or used and who accessed it.
You can use DRM to protect your media, software, and content in multiple ways. Here are a few DRM capabilities:
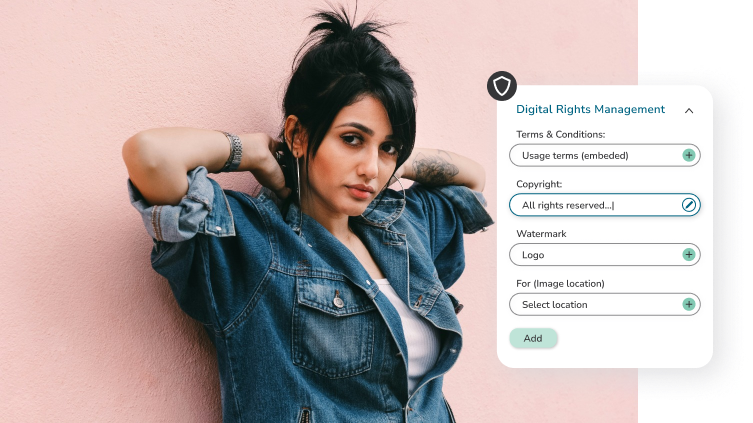
Why is digital rights management important?
Digital rights management (DRM) is important because it helps businesses and content providers protect their work from being used without permission. It makes sure that they get paid for their hard work and creativity. Without DRM, it’s easier for people to copy and share content illegally.
Companies can use DRM software to prevent unauthorized users from accessing sensitive documents or assets.
DRM also ensures correct usage of the organization’s brand assets, protecting both the brand and creators.
What are the types of digital rights management?
From copy protection to time-limited access, choosing the right type of DRM for your assets can be overwhelming. Here are the 11 major types of DRM:
1. Encryption
Encryption protects digital content by converting it into a secure encoded format. It transforms the original content using a complex algorithm into an unreadable form without the correct encryption code.
This encoded format is only accessible with the correct decryption key.
2. Digital watermarking
Digital watermarking means embedding a hidden digital marker into multimedia content like images, audio, or video. The marker is usually imperceptible during everyday use. Detection tools can extract or highlight the digital watermark.
Even if someone copies your content, digital watermarking provides content proof of ownership.
3. Governance
Governance means constructing rules for content use, such as limiting video viewing to specific countries or eBook downloads to a particular amount.
4. License agreements
Companies can guard their content and software by asking users to read and agree to their end-user license agreement the first time they access the content or software.
5. Authentication
Authentication requires users to validate their identity through the presentation of credentials such as:
6. Enforcement
Enforcement policies ensure people follow the rules you’ve set for your assets. If someone breaks the rules, there might be consequences like getting locked out of using content or software.
7. Copy protection
Copy protection stops people from copying your content without permission. Copy protection often involves using serial numbers or activation keys to limit the asset’s use to a specific user or computer.
8. License management
License management means tracking who has permission to use your content and how they use it. Proper management ensures that an organization adheres to the license or copyright terms, such as the number of users, specific usage rights, and expiration dates.
9. Time-limited access
Time-limited access means people can only use your content for a specific time amount. For example, they can access and watch a video online for 48 hours after they start watching.
10. Rights expression language
Rights expression language is a technical way of describing the rules for using your content. REL allows content providers to articulate precise rules regarding who can access digital content, under what conditions, and what users can do with that content once accessed.
11. Geographical limits
Geographical limits place boundaries on asset access by location.
What are the benefits of digital rights management?
No matter why you want to protect your digital assets, implementing DRM has six key benefits:
What are the challenges of not using digital rights management for your media?
Not using DRM solutions can bring several challenges, including online piracy, unauthorized use, and copyright infringement. Here are five challenges you will face without using DRM to protect your content:
What are the key use cases of digital rights management?
DRM works for many different types of teams and industries. Here are ten key digital rights management use cases:
1. eBooks and digital publishing
Publishers use DRM to protect their eBooks from being copied and shared. For example, when you create and distribute an eBook, DRM ensures your audience can’t share a copy with their colleagues for free.
2. Digital photography and art
Artists use DRM to protect their photos and artwork online. DRM protection helps them control who can use their images and ensure they get credit for their work. It’s also essential for organizations in the hospitality and travel industries that rely heavily on branded photography.
3. Video and music streaming services
Streaming services like Netflix or Spotify use DRM to control who can watch or listen to their content. That’s why you can’t just download and keep movies or songs from these services.
4. Software and video games
Software companies use DRM to prevent illegal copying of their programs and games. DRM also helps tech companies control and protect branded content.
5. Broadcasting
TV and radio broadcasters use DRM to manage the needs of large media libraries as media channel demands increase.
6. Digital libraries
Libraries use DRM to lend out and return digital books and resources.
7. E-commerce
Online stores use DRM to protect digital products like eBooks, music, or software. DRM helps prevent illegal sharing and ensures creators get paid for their work. It’s also vital for retailers that need to protect and distribute their brand content at scale.
8. Document security
Organizations use DRM to secure sensitive information, such as contracts, personal information, and protected data. DRM features are also essential for the healthcare creative teams to ensure their organization’s digital marketing assets are brand and compliant.
9. Mobile apps
App developers use DRM to protect their apps from being pirated. DRM helps them control how their apps are used and distributed.
10. Educational content
Schools and universities use DRM to manage access to digital textbooks and resources. DRM helps protect copyright and ensures that students use the content fairly. Educational institutions also use digital library software that includes DRM to protect their brand content.
Why choose digital asset management (DAM) and DRM
DRM is essential for protecting your branded content. But it doesn’t organize your content — the major challenge for organizations is still managing content at scale. It’s also hard to track content, copyright, and license data at scale.
That’s why you need a digital asset management (DAM) platform.
DAM makes it easy to organize, find, and share all your digital content from one centralized library. DAM’s DRM features include watermarks, user controls, and terms and conditions to keep your digital assets compliant and accessible to the right people.
The Beginner’s Guide to Digital Asset Management
Download the guide for free